Fluid Dynamics & Rheology
Featuring Dripping-onto-Substrate (DoS) Rheometry.Shear and Extensional Rheology. Interfacial Rheology. Non-Newtonian Fluid Mechanics
Ph.D. students: Jelena Dinic (Ph.D. 2018) and Leidy Nallely Jimenez (Ph.D. 2020) developed the dripping-onto-rheometry (DoS) rheometry protocols, with contributions initially by Yiran Zhang (Ph. D. 2016) and later by Carina Martinez (Ph.D. 2022). Current Ph.D. students including Cheryl Slykas, Lena Hassan, Nadia Nikolova, Louie Edano, Yash Vidyasagar, Andrew Rasmussen, and Somayeh Sepahvand continue to push the envelope in solving various experimental and analysis challenges for macromolecular engineering of formulations.
UG co-authors include Leidy Nallely Jimenez, Madeleine Biagoli, Thomas Mazur, (in prep or under review: Fahed Al-Breiki, Alexander Kubinski, Karim Al Zahabi, Miriam Jabr & Vihar Trada)
DoS RHEOMETRY
Capillary-driven thinning & pinch-off dynamics of complex fluids
Elastocapillarity. Finite-time Singularity. Self-Similarity. Printability. Jettability. Sprayability
Inertio-capillary, viscocapillary, elastocapillary, power law and terminal viscoelastocapillary thinning.
Influence of material properties and microstructure on fluid neck shape and shape evolution.
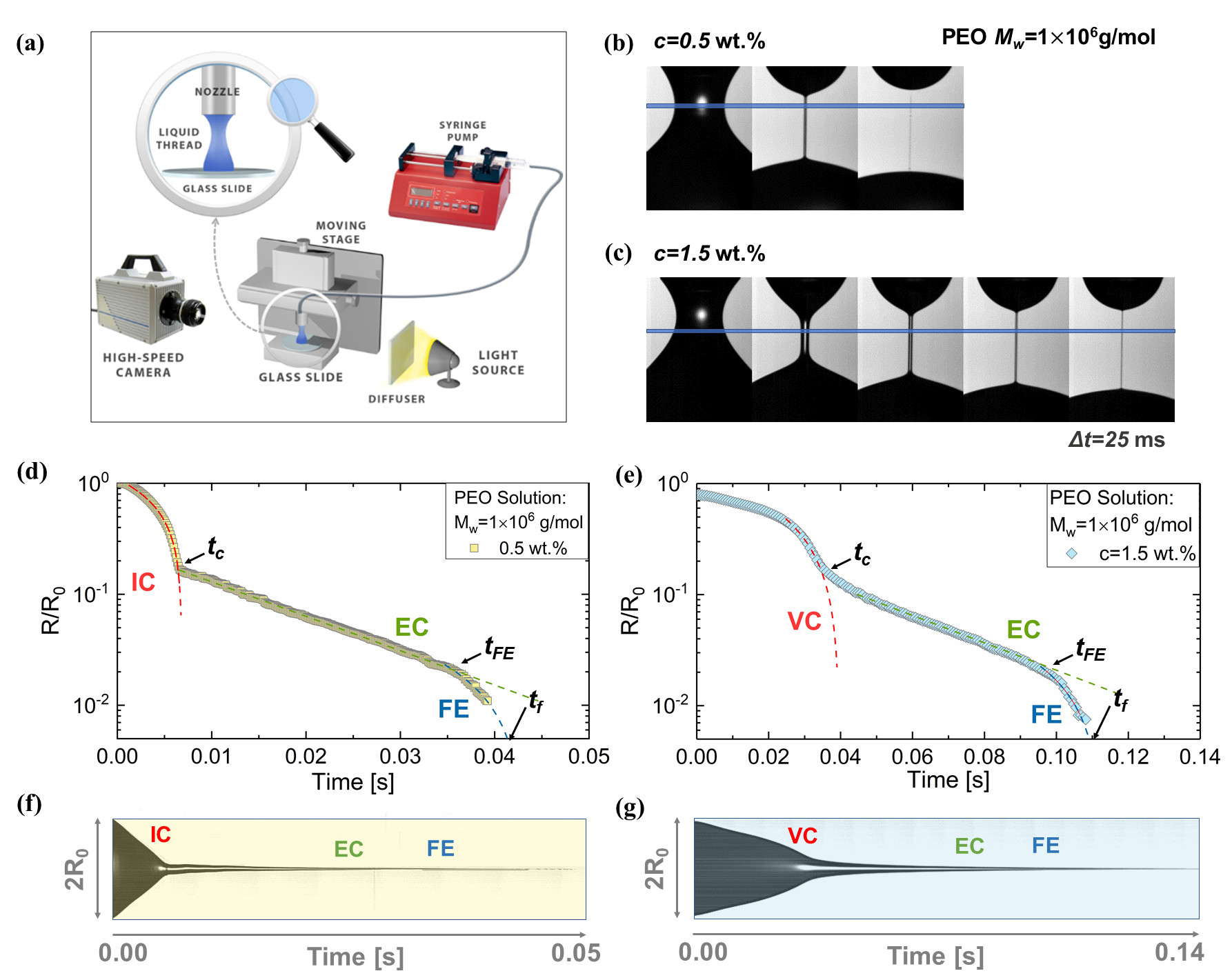
We introduced Dripping-Onto-Substrate (DoS) rheometry for characterizing capillarity-driven pinching dynamics and extensional rheology response of complex fluids. (Dinic et al., ACS MaroLett. 2015; Lab Chip, 2017)
Ongoing and recent work aims to connect heuristic quantities like jettability, sprayability, printability, spinnability, stickiness, stringiness, gloppiness, and ropiness to polymer physics, pinching dynamics, and non-Newtonian fluid mechanics.
FREE SURFACE FLOWS
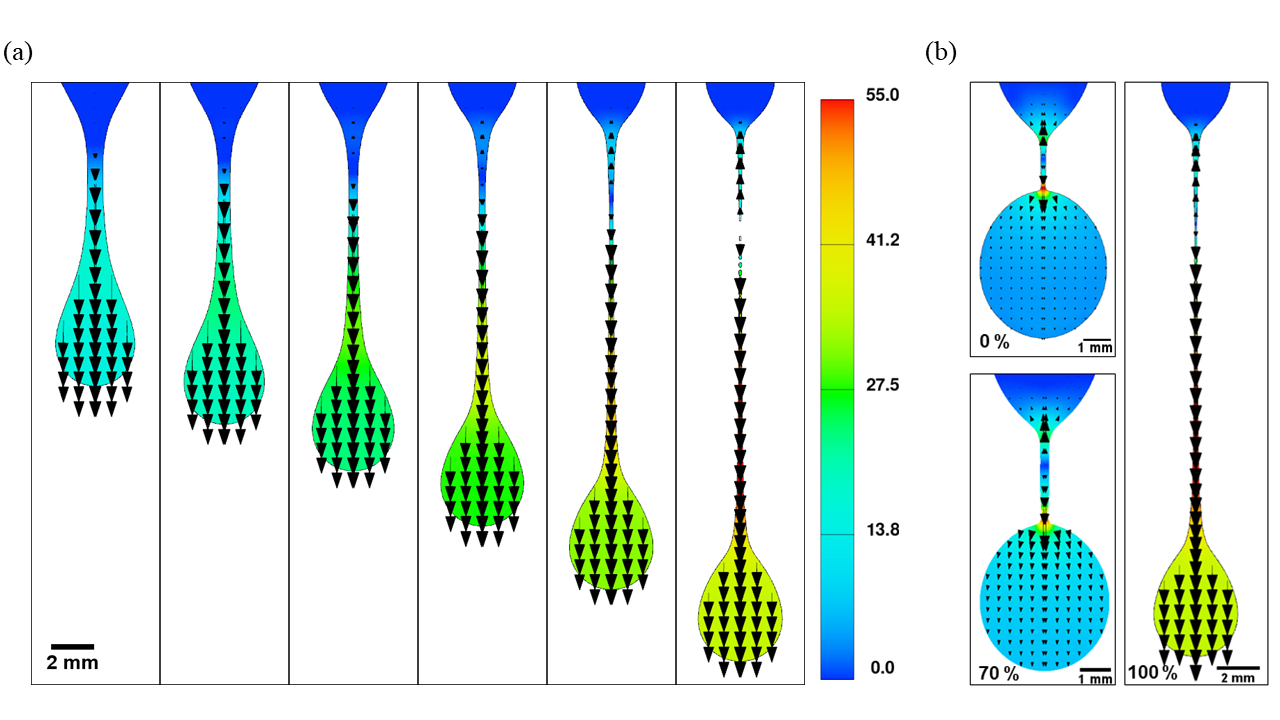
Volume-of-fluid based computational fluid dynamics using FLOW-3D
Capillarity-driven flows and pinch-off dynamics.
Figure source: Computational Analysis of Self-Similar Capillary-Driven Thinning and Pinch-off Dynamics during Dripping using Volume-of-Fluids Method, J. Dinic, and V. Sharma*, Physics of Fluids., (2019). ComputationalAnalysisofPinchOffFlow3DDripping
Publications from ODES-Lab featuring DoS Rheometry
1. “Extensional Relaxation Times of Dilute Polymer Solutions”, J. Dinic, Y. Zhang, L. N. Jimenez and V. Sharma*, ACS Macro Letters, 2015. tinyurl.com/ODES-DOS Dripping-onto-Substrate (DoS) Rheometry PDF
2.“Pinch-off Dynamics and Dripping-onto-Substrate (DoS) Rheometry of Complex Fluids”, J. Dinic, L. N. Jimenez and V. Sharma*, Lab Chip, 17, 460-473, 2017. Pinch-off Dynamics DosRheometry ComplexFluids PDF
3. “Pinch-off Dynamics and Extensional Relaxation Times of Intrinsically Semi-Dilute Polymer Solutions Characterized by Dripping-onto-Substrate (DoS) Rheometry”, J. Dinic, M. Biagioli and V. Sharma*, Journal of Polymer Science B Polymer Physics, 55, 1692-1704 (2017). DoSRheometry Intrinsically Semi-Dilute Solutions PDF
4. “Passive Nonlinear Microrheology for Determining Extensional Rheology”, K. W. Hsiao, J. Dinic, Y. Ren, V. Sharma and C. M. Schroeder*, Physics of Fluids, 29, 121603 (2017). Passive Microrheology DoS Rheometry PDF
5. Extensional Relaxation Time, Pinch-off Dynamics and Printability of Semi-Dilute Polyelectrolyte Solutions, L. N. Jimenez, J. Dinic, N. Parsi and V. Sharma*, Macromolecules, 51, 5191-5208 (2018). ExtensionalRheology Saltfree Semi-dilute PolyelectrolyteSolutions PDF
6. Effect of Salt Valency and Concentration on Shear and Extensional Rheology of Aqueous Polyelectrolyte Solutions for Enhanced Oil Recovery, A.V. Walter, L. N. Jimenez, J. Dinic, V. Sharma and K.A. Erk*, Rheologica Acta, 58, 145-157 (2019). PolyelectrolytesEOR_PDF
7. Macromolecular Relaxation, Strain and Extensibility Determine Elastocapillary Thinning and Extensional Viscosity of Polymer Solutions, J. Dinic and V. Sharma*, Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 116(18), 8766-8774 (2019). Extensibility DoS Rheometry PDF
8. Capillary Break-up and Extensional Rheology Response of Food Thickener Cellulose Gum (NaCMC) in Salt-Free and Excess Salt Solutions, L. N. Jimenez, C. Martinez Navaraez, and V. Sharma, Phys. Fluids, 32, 012113 (2020). ExtensionalRheol_CelluloseGum_PDF
9. Power Laws Dominate Shear and Extensional Rheology Response and Capillarity-Driven Pinching Dynamics of Entangled Hydroxyethyl Cellulose (HEC) Solutions, J. Dinic and V. Sharma*, Macromolecules, 53, 3424-3437 (2020)
10. Flexibility, Extensibility, and Ratio of Kuhn to Packing Length Dictate Pinch-off Dynamics, Coil-Stretch Transition, and Extensional Rheology of Polymer Solutions, J. Dinic and V. Sharma*, Macromolecules, 53, 4821-4835 (2020).
11. The rheologically-complex beauty of nail lacquer formulations, L. . Jimenez, C. D.V. Martinez Narvaez, Chenxian Xu, Samantha Bacchi, and Vivek Sharma, Soft Matter, 17, 5197-5213 (2021).
12. Rheology and pinching dynamics of associative polysaccharide solutions, C. D. V. Martínez Narváez, J. Dinic, X. Lu, C. Wang, R. Rock, H. Sun, and V. Sharma*, Macromolecules, 54, 6372-6288, 2021.
13. Dynamics and extensional rheology of polymer-surfactant association complexes, C. D. V. Martinez Narváez, T. Mazur, and V. Sharma, Soft Matter, 17, 6116-6126, 2021.
14. Evaporation and rheology chart a processability map for centrifugal force spinning, J. Merchiers, C. D. V. Martínez Narváez, C. Slykas, N.K. Reddy and V. Sharma†*, Macromolecules, in press, 2021.
Publications (not from UIC) using DoS Rheometry
Travis Walker’s Walker Research Group, University of South Dakota
K.A. Marshall, A.M. Liedtke, A.H. Todt and T.W. Walker. Extensional Rheometry with a Handheld Mobile Device. Experiments in Fluids, 58, 6, 2017.
K.A. Marshall and T.W. Walker, Investigating the dynamics of droplet breakup in a microfluidic cross-slot device for characterizing the extensional properties of weakly-viscoelastic fluids, Rheologica Acta, 2019.
Susan Muller’s Muller Lab at University of California, Berkeley
Y. Zhang and S. J. Muller, Unsteady sedimentation of a sphere in wormlike micellar fluids, Physical Review Fluids, 3, 043301, 2018.
Jonathan Rothstein’s Non-Newtonian Fluid Mechanics Lab, UMASS Amherst
S. Sur and J. Rothstein, Drop breakup dynamics of dilute polymer solutions: Effect of molecular weight, concentration, and viscosity, Journal of Rheology, 62, 1245 2018.
M. Rosello, S. Sur, B. Barbet and J. Rothstein, Dripping-onto-substrate capillary breakup extensional rheometry of low-viscosity printing inks, Journal of Non-Newtonian Fluid Mechanics, 266, 160-170, 2019.
S. Khandavalli, N. Sharma-Nene, S. Kabir, S. Sur, J. P. Rothstein, K. C. Neyerlin, S.A. Mauger, and M.. Ulsh, Towards optimizing electrospun nanofiber fuel cell catalyst layers: Polymer-Particle interactions and spinnability, ACS Applied Polymeric Materials, 2021.
Hadi Mohammadigoushki’s Complex Fluids Research Group at Florida State University
S. Wu and H. Mohammadigoushki, Sphere sedimentation in wormlike micelles: Effect of micellar relaxation spectrum and gradients in micellar extensions, Journal of Rheology, 62, 1061, 2018.
R. Omdivar, S. Wu and H. Mohammadigoushki, Detecting wormlike micellar microstructure using extensional rheology, Journal of Rheology, 63, 33, 2019.
S. Wu and H. Mohammadigoushki, Effect of moving contact line on filament pinch-off dynamics of viscoelastic surfactant fluids, Physical Review Fluids, 5, 053303, 2020.
S. Wu and H. Mohammadigoushki, Linear vs branched: flow of a wormlike micellar fluid past a moving sphere, Soft Matter, 17, 4395-4406, 2021.
Siva Vanapalli’s Microfluidic Laboratory at Texas Tech University
N. S. Suteria, S. Gupta, R. Potineni, S. K. Baier and eCapillary: a disposable microfluidic extensional viscometer for weakly elastic polymeric fluids, Rheologica Acta, 58, 403-417, 2019.
Howard A. Stone’s Complex Fluids Laboratory at Princeton University
M. Y. Pack, A. Yang, A. Perrazo, B. Qin and Role of extensional rheology on droplet bouncing, Physical Review Fluids, 4, 12363, 2019.
Vivek Sharma’s and ODES-lab’s Rheology Papers (in addition to the DoS rheometry publications)
Dripping using Volume-of-Fluids Method implemented in FLOW-3D: “Computational Analysis of Self-Similar Capillary-Driven Thinning and Pinch-off Dynamics during Dripping using Volume-of-Fluids Method”, J. Dinic, and V. Sharma*, Physics of Fluids, (2019). ComputationalAnalysisofPinchOffFlow3DDripping
Influence of Hydrophobic modification in Polysaccharide Rheology and introduces ROJER: “The Rheology of Aqueous Solutions of Ethyl Hydroxy-Ethyl Cellulose (EHEC) and its Hydrophobically Modified Analogue (hmEHEC): Extensional Flow Response in Capillary Breakup, Jetting (ROJER) and in a Cross-Slot Extensional Rheometer”, V. Sharma*, S.J. Haward, J. Serdy, B. Keshavarz, A. Söderlund, P.Threlfall-Holmes and G. H. McKinley, http://tinyurl.com/ROJERJetting Soft Matter, 11, 3251-3270 (2015). ROJER PDF
Utilizes ROJER to quantify extensional rheology response: “Studying the Effects of Elongational Properties on Atomization of Weakly Viscoelastic Solutions Using Rayleigh Ohnesorge Jetting Extensional Rheometry (ROJER),” B. Keshavarz, V. Sharma, E. C. Houze, M. R. Koerner, J. R. Moore, P. M. Cotts, P. Threlfall-Holmes and G. H. McKinley, JNNFM, 2015.
Abnormal rule = Laun’s rule plus forgotten Cox-Merz Rules “An intriguing empirical rule for estimating the first normal stress difference from steady shear viscosity data for polymer solutions and melts,” V. Sharma* and G. H. McKinley, Rheologica Acta, 51 (6), 487-495 (2012) Abnormal Rule PDF
Connects spinnability to shear and extensional rheology studies “Shear and extensional rheology of cellulose in ionic liquids”, S. J. Haward*, V. Sharma, G. H. McKinley and S. Rahatekar, Biomacromolecules, 13, 1688-1699 (2012). Cellulose/Ionic Liquids PDF
Introduces interfacial creep ringing and influence on surfactant on interfacial viscoelasticity of proteins “Apparent bulk yield stress, interfacial creep ringing and interfacial viscoelasticity of globular protein/surfactant mixtures,” A. Jaishankar, V. Sharma and G. H. McKinley, Soft Matter, 7 (17), 7623-7634 (2011). PDF Protein-Surfactant Interfacial Rheology & Creep Ringing
Establishes how interfacial viscoelasticity of proteins can influence the measured shear rheology response: “Rheology of Globular Proteins: Apparent yield stress, interfacial viscosity and high shear rate viscosity of Bovine Serum Albumin Solutions,” V. Sharma, A. Jaishankar, Y. Wang and G. H. McKinley*, Soft Matter, 7 (11), 5150-5160 (2011). Protein Rheology PDF
Explores the use of flow-induced birefrinegence for quantifying extensional viscosity and stress-optical coefficient: “Extensional opto-rheometry with biofluids and ultra-dilute polymer solutions”, S.J. Haward, V. Sharma and J. A. Odell, Soft Matter, 7 (21), 9908-9921 (2011). Cover Art PDF Extensional Opto-Rheometry
Explores jet break-up using Oldroyd-B and Giesekus models: “Dynamics of bead formation, filament thinning and breakup in weakly viscoelastic jets,” A. M. Ardekani, V. Sharma and G. H. McKinley, Journal of Fluid Mechanics, 665, 46-56 (2010) PDF