ODES-lab: Polymer Physics
Dynamics of stretched chains.Shear and Extensional Rheology. Interfacial Rheology. Polymer & Protein Physics. Suspensions & Formulations.
Ph. D. students: See papers by Jelena Dinic (Ph.D. 2018) on neutral and by Leidy Nallely Jimenez (Ph.D. 2020) on charged polymers for a comprehensive analysis of extensional relaxation time and stretched polymer physics. See papers led by Nallely Jimenez on food gums and nail lacquers, by Carina Martinez (Ph.D. 2022) on model paint fluids and polymer-surfactant mixtures, and ongoing work from Lena Hassan and Nadia Nikolova on food formulations. See publications by Cheryl Slykas and Carina Martinez (Ph. D. 2022) on connections between macromolecular properties, rheology, spinnability, and fiber properties. Current Ph. D. students Louie Edano and Cheryl Slykas are exploring the spinnability of composite fibers, whereas Somayeh Sepahvand is examining rheology of food gums while Yash Vidyasagar investigates the problem of spray drift and polymer-surfactant interactions.
UG co-authors include Leidy Nallely Jimenez, Madeleine Biagoli, Thomas Mazur, (in prep or under review: Fahed Al-Breiki, Alexander Kubinski, Karim Al Zahabi, Miriam Jabr & Vihar Trada)
STRETCHED POLYMER PHYSICS
Role of Excluded Volume, Hydrophobic, Topological and/ or Hydrodynamic Interactions
Influence of flexibility, extensibility, molecular weight, and concentration on polymer dynamics.
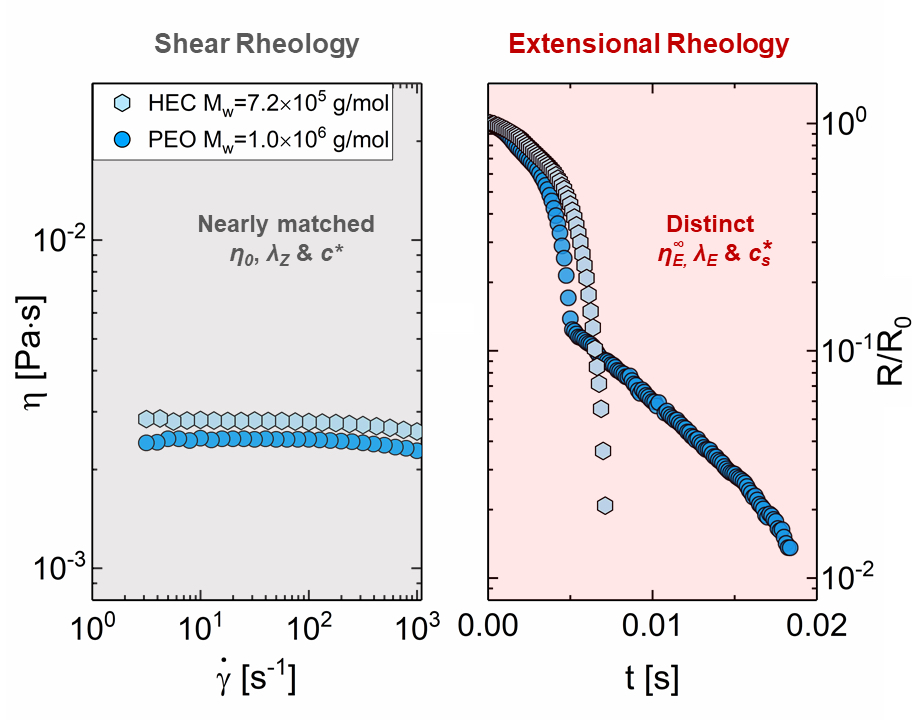
Extensional relaxation time displays concentration-dependent variations quite distinct from shear relaxation time.
Contributions
Extensional relaxation times measured for unentangled solutions exhibit concentration-dependence distinct from shear rheology response, or anticipated by blob models, developed for the relaxation of weakly perturbed chains.
For neutral polymers, we identified a stretched overlap concentration below which the extensional relaxation time is concentration independent.
We showed that the influence of polymer choice could be evaluated a priori, using three macromolecular parameters: flexibility, extensibility, and segmental dissymmetry, defined as the ratio of packing length to Kuhn length.
POLYELECTROLYTES
Electrostatic and hydrophobic interactions. Influence of solvent and salt.
Shear, extensional, and interfacial rheology of proteins and charged polymers.
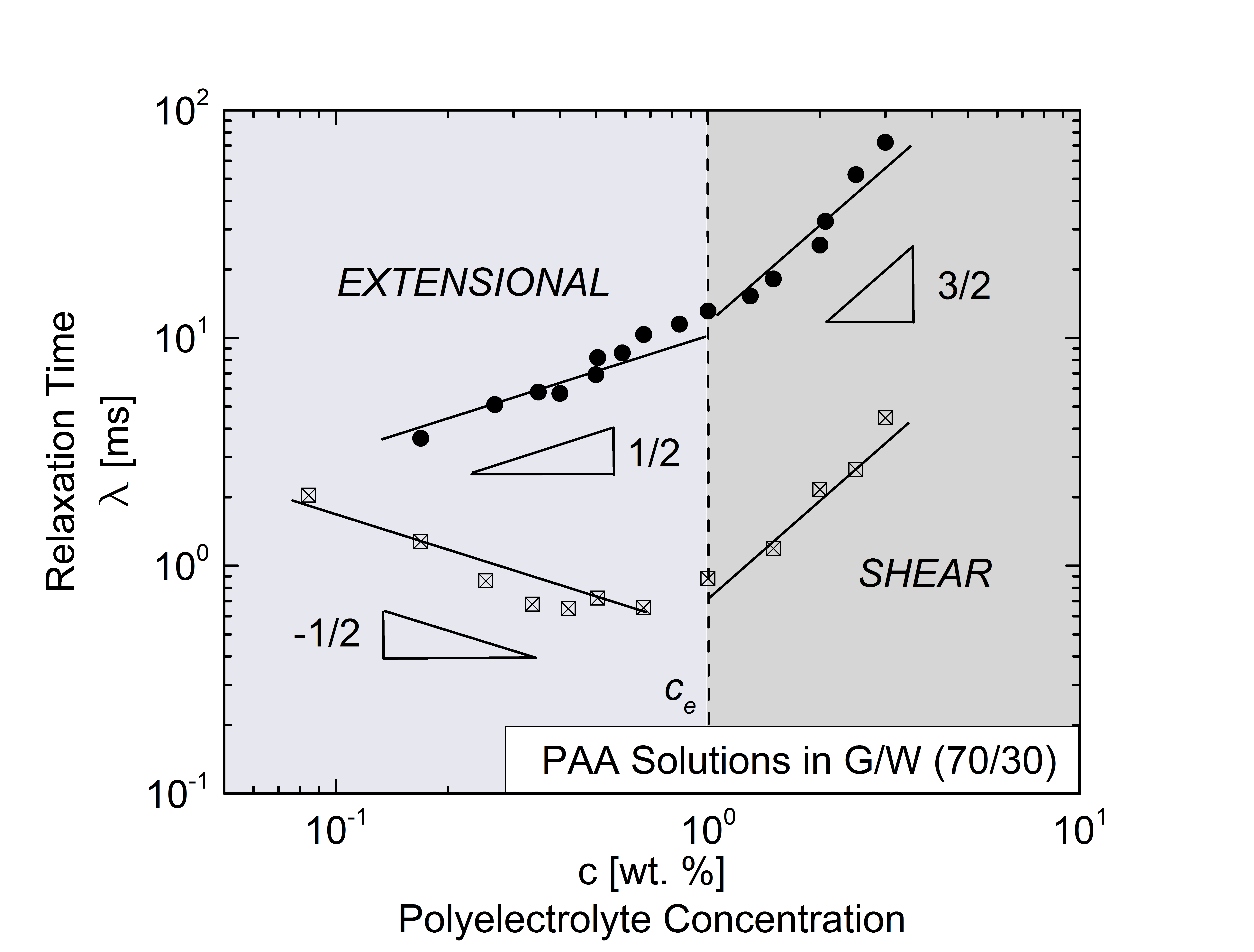
Graphic Abstract for Extensional Relaxation Time, Pinch-off Dynamics and Printability of Semi-Dilute Polyelectrolyte Solutions, L. N. Jimenez, J. Dinic, N. Parsi and V. Sharma*, Macromolecules, 51, 5191-5208 (2018). ExtensionalRheologySaltfreeSemidilutePolyelectrolyteSolutions
FIBER SCIENCE & ENGINEERING
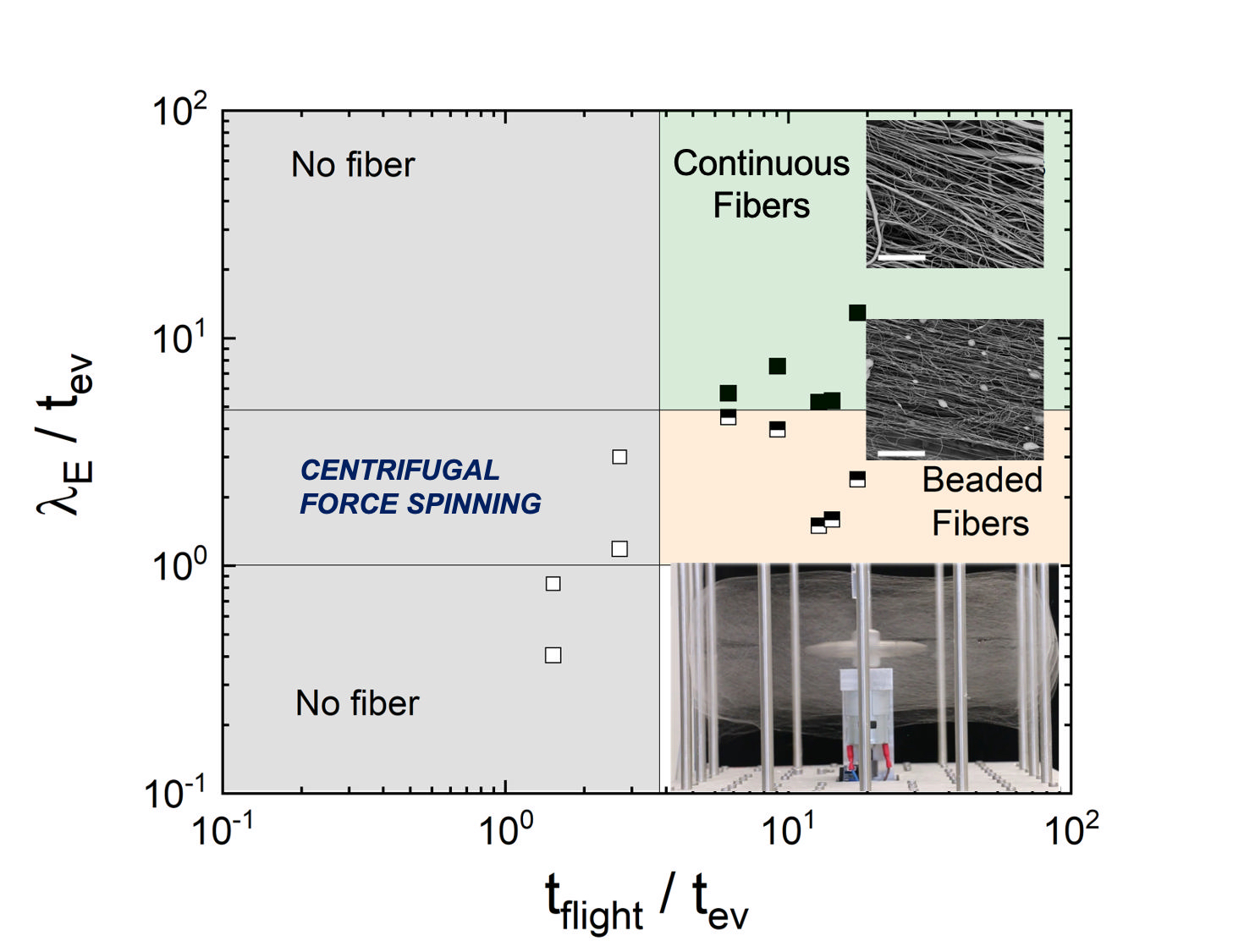
Centrifugal force spinning | Spinnability | Macromolecular engineering of fiber properties | Membrane engineering
Making fibers using “the cotton candy” process.
Extensibility-enriched spinnability. Volatile-entangled spinnability.
Mechanical properties and crystallinity of fibers. Sorption.
See publications connecting our rheology and polymer physics ideas to centrifugal force spinning research carried out by our collaborators (formerly in the University of Hasselt, Belgium): Jorgo Merchiers (who finished his Ph.D. in 2021) and his advisor, Naveen Reddy. We identified two distinct mechanisms underlying spinnability: volatile-entangled and extensibility-enriched.